Exactly How CCTV Cameras With Fiber Optic Outcome Boost Long-Distance Surveillance
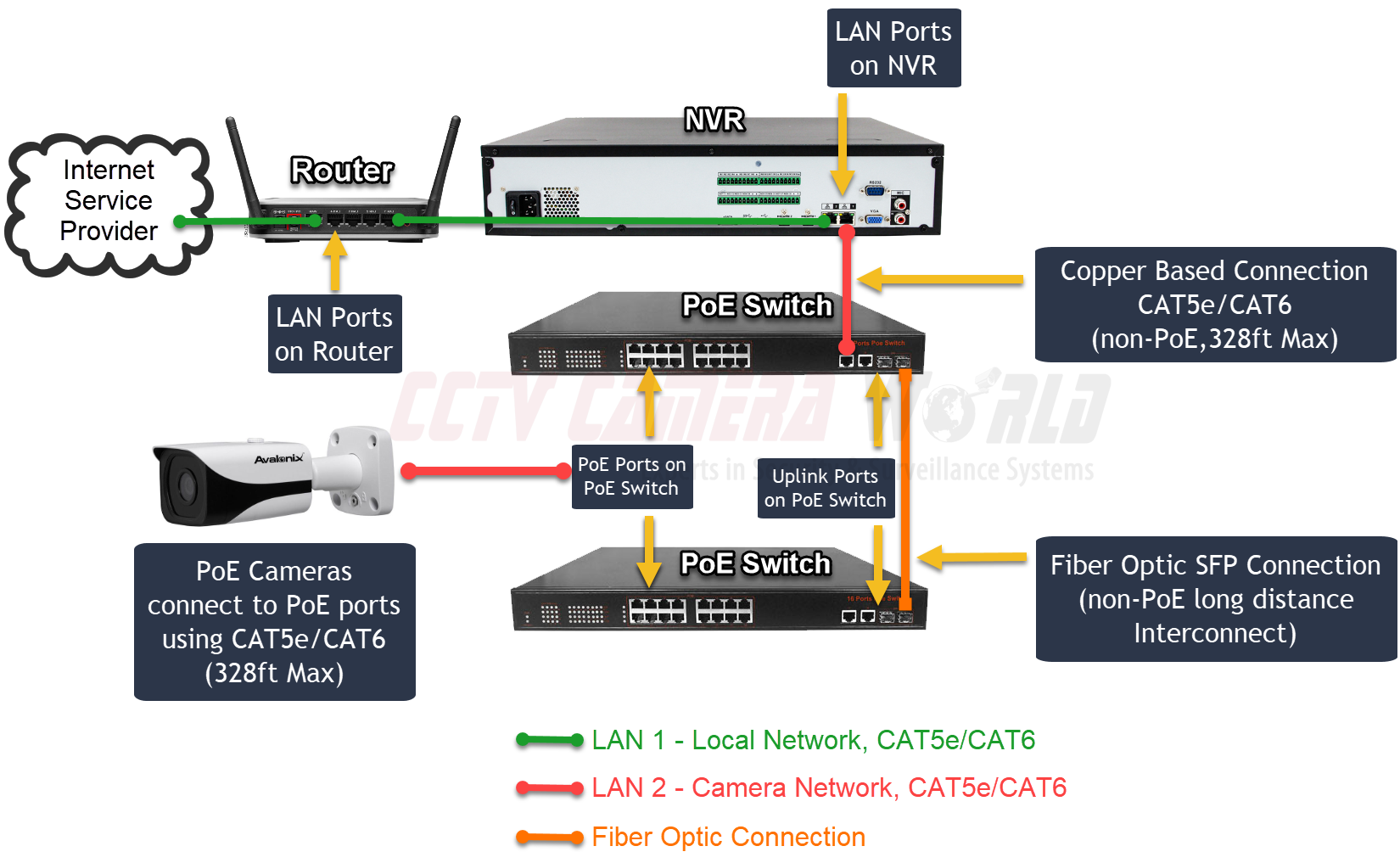
CCTV video cameras geared up with fiber optic output stand for a substantial improvement in long-distance monitoring modern technology, using unequaled advantages over traditional systems. By leveraging the buildings of light transmission via fiber optics, these cams make sure high-definition video top quality continues to be intact across substantial ranges while successfully minimizing electro-magnetic interference - cctv fibre optic cable.

Understanding Fiber Optic Innovation
Fiber optic innovation is significantly made use of in long-distance surveillance applications as a result of its exceptional capacity for information transmission. This modern technology employs slim hairs of glass or plastic fibers to transfer data as light signals, substantially minimizing the attenuation typically related to conventional copper cords. The intrinsic residential properties of fiber optics allow for the transmission of large quantities of information over considerable ranges without loss of top quality, making it a suitable option for applications needing dependable communication.
The concept of total inner reflection facilitates the reliable transmission of light within the fiber, guaranteeing high bandwidth and rate. Unlike electrical signals in steel wires, fiber optics are unsusceptible to electromagnetic disturbance, improving the integrity of data transmission. This particular is especially beneficial in atmospheres with high degrees of electrical sound, such as industrial setups or urban locations.
In addition, fiber optic cords are lighter and more versatile than their copper equivalents, which simplifies installment and decreases architectural load. With their longevity and resistance to environmental variables, optical fiber are fit for outside applications, therefore extending the reach of checking systems. Consequently, fiber optic innovation is coming to be a cornerstone in contemporary security solutions, successfully addressing the difficulties of long-distance surveillance.
Benefits of Fiber Optic CCTV
Using fiber optic technology in CCTV systems provides many benefits that enhance monitoring capacities. Among the primary benefits is the capability to transmit high-definition video over fars away without significant signal destruction. Unlike conventional copper cable televisions, optical fiber can keep video top quality over substantial runs, making them perfect for big residential or commercial properties or remote monitoring locations.
Additionally, fiber optic cable televisions are less vulnerable to electromagnetic interference, which can distort signals in standard systems. This makes certain more clear photos and undisturbed solution, important for protection surveillance. Fiber optics are inherently extra safe and secure, as obstructing signals needs specialized tools, therefore offering an extra layer of defense versus unauthorized access.
The light-weight and compact nature of fiber optic cables additionally simplifies installation, enabling less complicated transmitting through limited areas and decreasing overall labor prices. Their durability makes them immune to environmental variables such as dampness and temperature level fluctuations, extending the life expectancy of the surveillance system.
Last but not least, fiber optic systems can sustain a majority of cams on a solitary network, optimizing sources and providing scalability for future growth. These benefits make fiber optic CCTV systems a premium option for modern security needs.
Contrast With Conventional Systems
When contrasting CCTV systems, conventional setups commonly fall short in numerous essential areas, specifically in regards to distance and signal honesty. Conventional coax systems normally face considerable signal deterioration over fars away, restricting effective surveillance ranges to about 300 feet (cctv fibre optic cable). Beyond this limit, picture clarity decreases, resulting in prospective blind spots and decreased see this site security effectiveness
In comparison, fiber optic systems keep signal integrity over a lot greater distances, commonly going beyond several miles without loss of high quality. This is largely due to their capability to transfer information as light signals, which are less vulnerable to electro-magnetic interference than electrical signals made use of in conventional systems.
Furthermore, typical systems require much more considerable upkeep and troubleshooting due to their vulnerability to ecological variables such as wetness and electromagnetic noise. Fiber optic systems, conversely, offer enhanced resilience and lower maintenance costs, as they are much less vulnerable to damages.
Applications in Long-Distance Surveillance
The find more info benefits of modern-day CCTV systems in preserving signal stability over long distances open up a variety of applications for long-distance surveillance. One substantial application remains in metropolitan monitoring, where towns deploy fiber optic CCTV systems to monitor public spaces, enhancing safety and security and hindering criminal task. These systems supply continuous, top quality video feeds that are crucial for reliable police and emergency situation reaction.
One more essential application remains in industrial settings, where remote tracking of manufacturing processes and unsafe areas is vital. Fiber optic CCTV can endure extreme settings and transfer information over cross countries without loss of high quality, allowing for real-time oversight and decreasing dangers to personnel.
In addition, crucial framework such as airports, trains, and pipes take advantage of long-distance CCTV tracking. Safety and security groups can supervise huge areas from streamlined control spaces, making sure fast feedback to any type of incidents.
Additionally, in agricultural settings, farmers use long-distance CCTV to keep track of crops and livestock, helping to improve efficiency and safety and security. On the whole, the versatility and reliability of fiber optic CCTV systems make them crucial across different sectors, enabling comprehensive monitoring options tailored to certain requirements.
Future Patterns in Security Technology
Exactly how will improvements in modern technology improve the landscape of security? The future of surveillance modern technology is poised for substantial improvement, driven by innovations such as expert system (AI), artificial intelligence, and side computing. These technologies enable real-time data analysis, permitting rapid identification of prospective dangers and enhanced situational awareness.
AI-powered analytics will certainly boost the precision of face recognition systems, minimizing incorrect positives and making it this article possible for more efficient monitoring of people. Moreover, the combination of Net of Things (IoT) tools will assist in a smooth network of interconnected monitoring systems, boosting monitoring capabilities across substantial areas.
Another trend is the shift in the direction of cloud-based storage space solutions, which use scalable information monitoring and ease of access. This will certainly enable companies to save huge quantities of video clip information without the limitations of physical storage, while making sure that details is conveniently retrievable.
Verdict
In verdict, CCTV cams furnished with fiber optic output stand for a significant innovation in long-distance tracking capacities. As monitoring modern technology continues to evolve, the adoption of fiber optic remedies will likely play an essential duty in improving protection across diverse applications.